Functional Nutritional Profile

Functional Nutritional Profile
€335.00 + phlebotomy and shipping
Testing your levels of these key nutrients will allow your nutritionist to identify any gaps you may have and tailor their nutritional recommendations to meet your specific requirements.
Who can benefit from this test?
As this is a test of a wide range of vitamins and minerals, it is useful for optimising general health or with respect to a certain health condition, optimising your fertility or for healthy ageing.

Learn More about our Functional Nutritional Profile
Blood test (phlebotomy)
The functional nutritional profile is a comprehensive analysis of a number of minerals, vitamins, fatty acids and antioxidants in the body. Measuring your nutritional status is important for many chronic conditions and even just for general health. This allows your Nutritionist to tailor your nutrition and supplement plan for a targeted approach.
Phlebotomy can be carried out at our Dublin clinic or locations around the country. Please enquire with our team. Phlebotomy carries an additional charge.
This test measures:
- Minerals (in whole blood): zinc, selenium, copper, zinc, calcium, red cell magnesium, potassium and ferritin as a measure of iron stores
- Serum vitamins: vitamin A, Vitamin E, Vitamin D
- Omega-3 index: measurement of 25 different fatty acids as a marker of anti-inflammatory and protective omega-3 fats in red cell membranes versus pro-inflammatory omega-6, saturated fats, trans fatty acids.
- Antioxidant status: super oxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX)
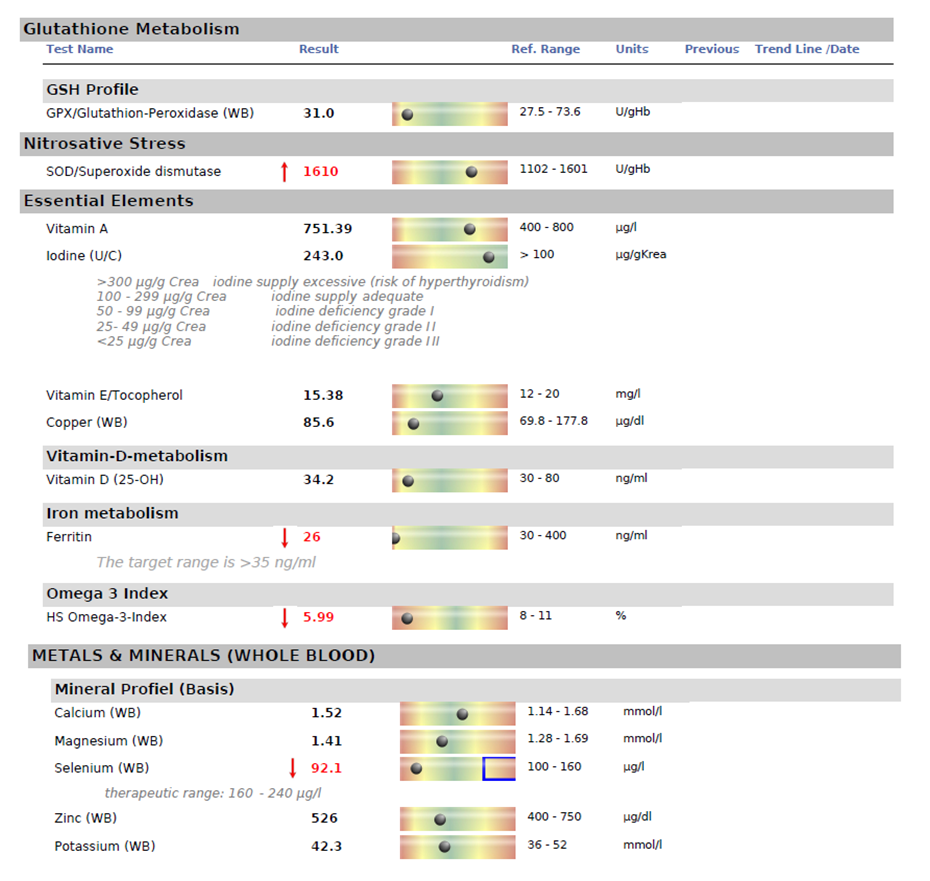
Miranda did a Functional Nutritional Profile blood test to optimise her nutrient status as she was trying to conceive. An personalised dietary and supplement protocol was designed to address her deficiencies and optimise nutrients for pregnancy.
Key Findings:
- Elevated levels of oxidative stress were detected which can impact on egg quality and health of the embryo
- Iron stores were low which would be important to correct before pregnancy
- Vitamin D was low normal, important for health of the pregnancy and development of the foetus, especially if pregnant over the winter months
- Iodine levels were optimal for pregnancy
- Low levels of selenium which can impact the immune system
- Low levels of omega-3 which was due to absence of fish in the diet