Hormone DNA Risk Profile

Hormone DNA Risk Profile
€100 interpretation fee as add-on to DUTCH Comprehensive Hormone test
DNA analysis can give valuable information about whether genetic factors are important for your hormonal balance, and why a protocol may or may not be working for you. It can also give information on which elements of hormonal detoxification might need long term support.
Who can benefit from this test?
Your nutritionist may have recommended this test as an add-on to your DUTCH Comprehensive Hormone test if you have:
- Hormonal conditions such as PCOS, fibroids and endometriosis
- PMS, PMDD
- Perimenopause, menopause, irregular cycles
- Personal or family history of breast cancer, ovarian cancer, prostate cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia or other hormone related cancers
- An interest or concern about liver detoxification, MTHFR and COMT methylation genes

Learn More about our Hormone DNA Risk Profile
DNA test (Ancestry DNA, 23andMe or MyHeritage)
A basic DNA test can be carried out using one of the suppliers – we usually recommend Ancestry DNA as it covers most of the relevant genes for this analysis.
We can mine your DNA data for SNPs or single nucleotide polymorphisms which are minor changes to the DNA sequence. These are extremely common and give us much of our genetic individuality. Some changes will be favourable, and others can reduce activity of certain genes or enzymes, increasing risk for hormonal imbalances, hormonal conditions and certain cancers.
Using this information, we relate your genetic risk factors to the hormone levels and pathways as identified on your DUTCH Comprehensive Hormone Test. This gives important information on how you might be able to modify these pathways, and which might be an important focus for you due to your genetic predisposition.
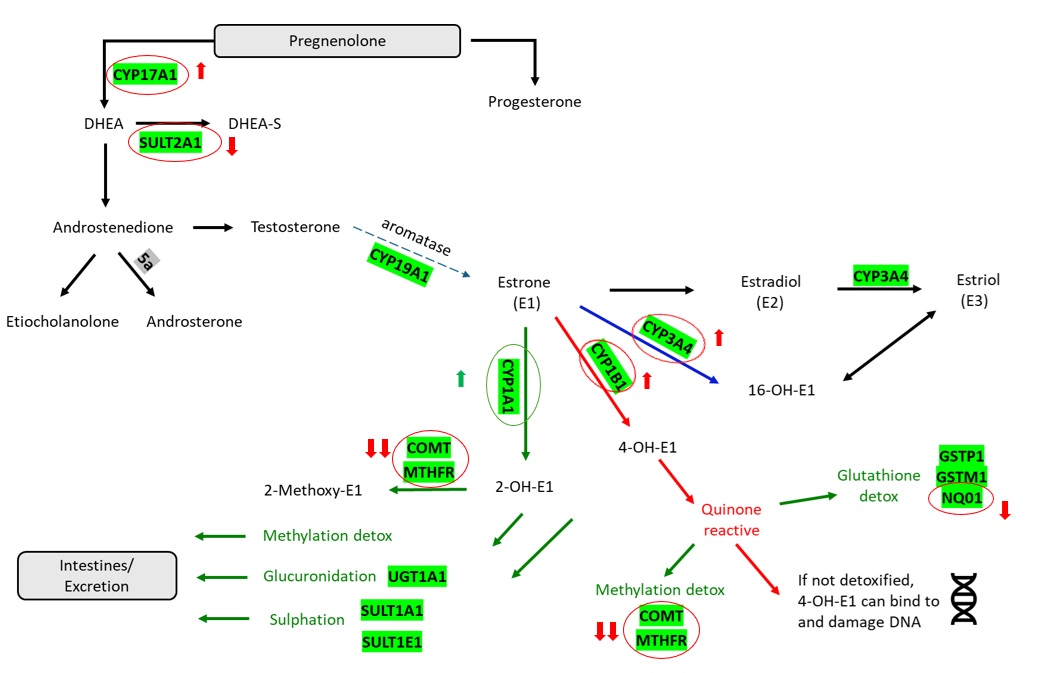
This test measures:
- CYP171A1 and SULT2A1 genes important for DHEA and testosterone levels
- CYP19A1 or aromatase gene which converts testosterone to oestrogen, important in men and women
- CYP3A4, CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 which detoxify oestrogen (phase I), the CYP1A1 being the safest detoxification route
- Phase II detoxification genes to safely excrete oestrogen including glucuronidation, glutathione and sulphation genes
- Comprehensive analysis of several COMT and MTHFR methylation genes which also play important roles in the cell cycle, folate cycle and DNA synthesis
Yasmine had a family history of breast cancer and experienced many hormonal symptoms such as PMS and irregular cycles. She had not been diagnosed with PCOS but her DUTCH Comprehensive Hormone test showed that she had higher than average testosterone levels. Her levels of oestrogen were high and though her phase I detoxification was good, her methylation levels were low.
The DNA analysis confirmed that she had a predisposition for elevated and active levels of DHEA, driving high testosterone and oestrogen levels. It would be extra important to ensure safe detoxification of high levels of hormones. Her ‘good’ CYP1A1 pathway was working well but she also had some increased risk for the other less favourable pathways.
Most importantly, she was homozygous for the MTHFR mutation and this was coupled with several ‘slow’ COMT mutations. Her methylation was impaired and needed a high level of support. The NQ01 detoxification pathway was likely impaired also so extra support was required, particularly given her family history.
Key Findings:
- Heterozygous (one copy of risk gene) for CYP17A1 and heterozygous for SULT2A1 = higher levels of circulating active DHEA leading to increased risk of high testosterone
- Heterozygous for CYP1B1 and CYP3A4 increasing enzyme activity in oestrogen detoxification pathway toward the less safe 4-OH and 16-OH pathways
- Homozygote (two copies of the risk gene) for MTHFR at the C667T SNP which may reduce the activity of the MTHFR gene by up to 70%. This is an important methylation pathway and requires ongoing support
- Heterozygous for three different COMT SNPs which may reduce activity of this key methylation enzyme
- Heterozygous for NQ01 which may result in reduced activity of this antioxidant in hormone detoxification